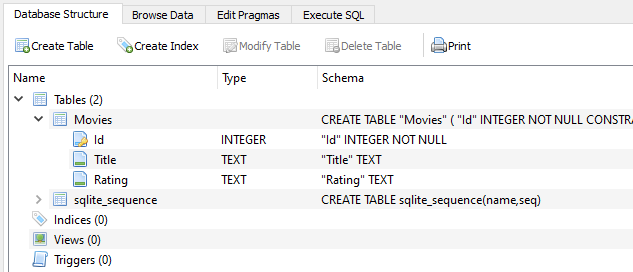
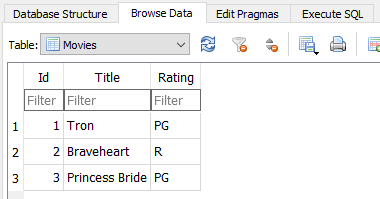
- Create - Add a new movie
var movie = new Movie
{
Title = "Tron Legacy",
Rating = "PG-13"
};
using (var db = new MovieTheaterContext())
{
db.Movies.Add(movie);
// Saving changes automatically assigns a new Id to movie
db.SaveChanges();
}
- Read - Read all movies
var movieList = new List<Movie>();
// Add all movies from database to movieList
using (var db = new MovieTheaterContext())
{
foreach (var movie in db.Movies)
{
movieList.Add(movie);
}
}
- Update - Change an existing movie
// Assume movie.Id is set to an existing database movie
movie.Title = "Tron Returns";
movie.Rating = "PG";
using (var db = new MovieTheaterContext())
{
db.Movies.Update(movie);
db.SaveChanges();
}
- Delete - Delete an existing movie
// Assume movie.Id is set to an existing database movie
using (var db = new MovieTheaterContext())
{
db.Movies.Remove(movie);
db.SaveChanges();
}